Mixing Vessels SUPERBLEND
- HOME
- Products & Solutions
- Mixing Vessels
- SUPERBLEND
SUPERBLEND cleared an inconsistency between the laminar flow and turbulent flow using the 2-shaft mechanism.
Multipurpose mixer that exceeds the limitation of the vertical-type mixing vessel.
The homogeneous mixing from low viscosity to high viscosity, which was a critical issue of the mixing vessel, was attained by the 2-shaft mechanism with different impeller shapes. This mechanism always offers the optimum operations for an abrupt change of viscosity that is caused at multiproduct production or polymerization.
CHECK POINT 01 Variation of mixing time for liquid viscosity
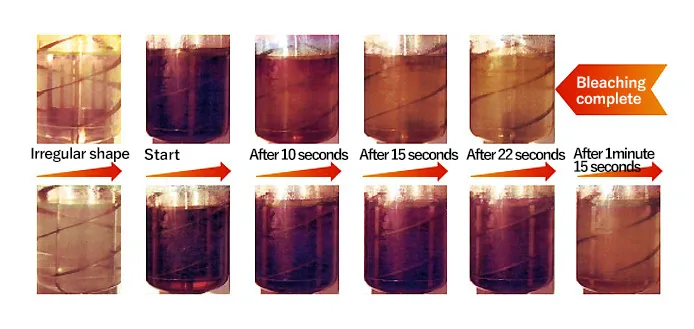
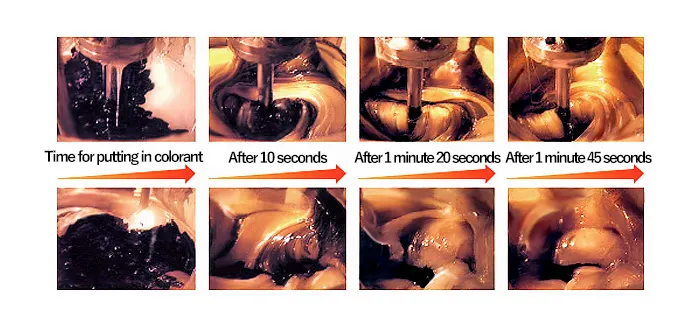
For polymerization reaction, dissolution, or crystallization, the liquid viscosity in the vessel is changed significantly during operation. The impeller appropriate in the normal highest viscosity range is selected, but the operation time is influenced if the homogeneous distribution fails during initial operation. This influence is a point that cannot be ignored. The photo shows the decolorization status with low viscosity and high viscosity liquid. For the double helical ribbon impeller, the mixing performance for low viscosity reduces excessively.
Figure 1 shows a variation of the mixing time with low viscosity. As shown in the figure, the SUPERBLEND has the appropriate characteristics in the range from low viscosity to high viscosity.
| SUPERBLEND | DOUBLE HELICAL RIBBON | |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing conditions | Viscosity 10 poise | |
| Rotation speed | Inner impeller: 104 rpm Outer impeller: 52 rpm |
75 rpm |
|
||
| SUPERBLEND | DOUBLE HELICAL RIBBON | |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing conditions | Viscosity 5000 poise | |
| Rotation speed | Inner impeller: 13 rpm Outer impeller: 13 rpm |
15 rpm |
|
||
Comparison of SUPERBLEND and DOUBLE HELICAL RIBBON
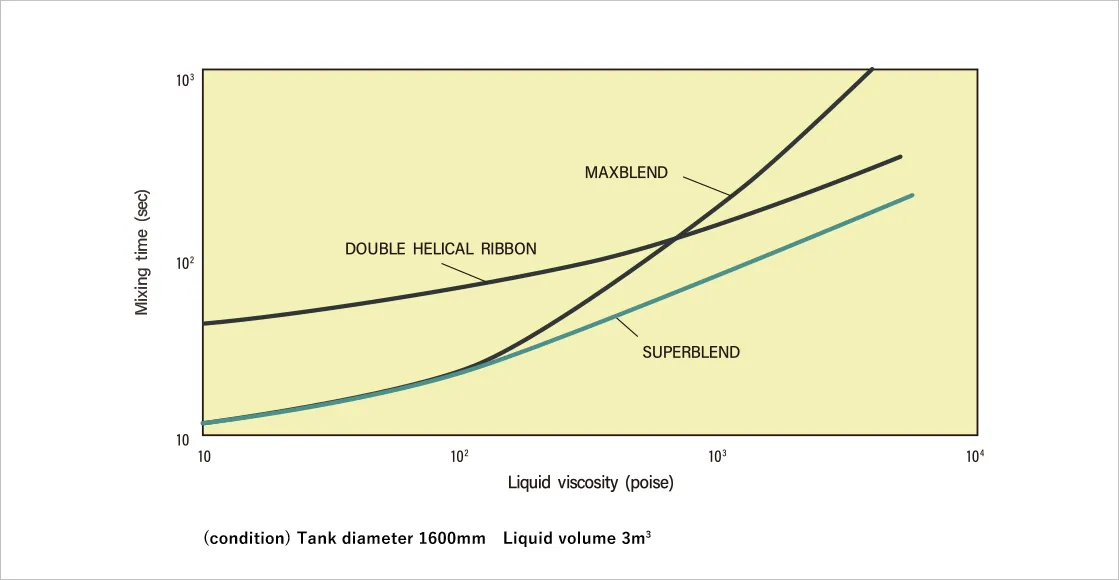
Figure 1. Mixing time change due to fluid viscosity
When consumption power Pv(kW/m3) is fixedCHECK POINT 02 Comparison of complete mixing time for different viscous liquids
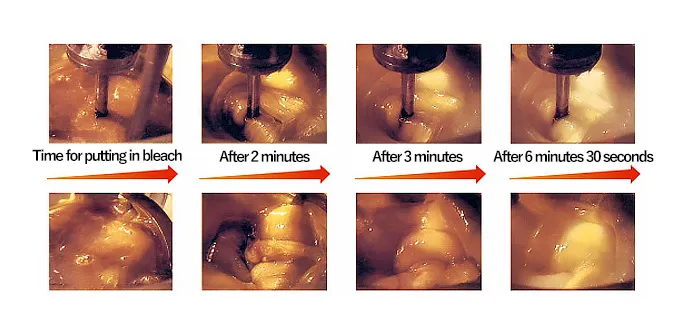
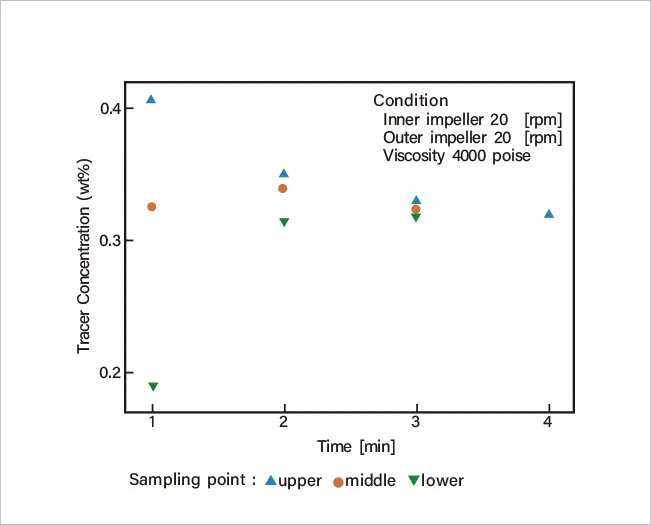
The photo shows the status in which low-viscosity liquid is involved in high-viscosity liquid. In the SUPERBLEND, low-viscosity liquid is easily involved in high-viscosity liquid by the synergistic effect of the inner and outer impellers. Figure 2 shows the relation between the density distribution and mixing time of the involved liquid. Like this, the SUPERBLEND enables a short-time liquid dispersion in high viscosity.
| SUPERBLEND | DOUBLE HELICAL RIBBON | |
|---|---|---|
| Mixing conditions | Viscosity 5000 poise | |
| Rotation speed | Inner impeller: 13 rpm Outer impeller: 13 rpm |
15 rpm |
|
||
Comparison of SUPERBLEND and DOUBLE HELICAL RIBBON
INFORMATION Related Information
-
 Plant Engineering
Plant Engineering
We propose our best performance with integration of our engineering solution and our core technologies, those are substantiated with our several decades career in the plant engineering fields.
-
 Technical Services
Technical Services
It is possible to obtain test data under any operating conditions using many kind of test facilities.
So, we will can evaluate and propose optimum mixing power as well as equipment specification for scaled-up or scaled-down model. -

The more you learn the mixing, the more mysteries you find.
Sumitomo Heavy Industries Process Equipment, mixing specialist, will provide clear explanations on the basics of mixing techniques and how to select mixing devices.